

SMITH CHART TUTORIAL SERIES
( ) ( )0 0 0 0(d) dZ Z z Z r j x Z r j Z x= + = +Īmanogawa, 2000 - Digital Maestro Series 148 ( )dz r j x= +and the actual impedance is Read the values of the normalized resistance r and of thenormalized reactance x that correspond to the reflectioncoefficient point. Determine the complex point representing the givenreflection coefficient (d) on the chart.Ģ. This vector represents the reflection coefficientĪmanogawa, 2000 - Digital Maestro Series 147ġ. The chart providesdirectly the magnitude and the phase angle of (d)Īmanogawa, 2000 - Digital Maestro Series 146Ĥ.

The intersection of the two curves indicates the reflectionĬoefficient in the complex plane. Find the arc of constant normalized reactance x4.
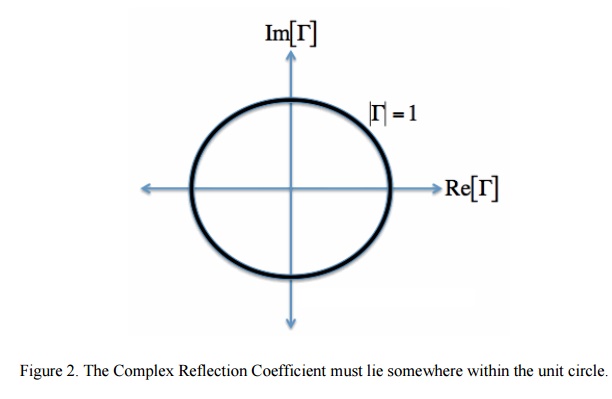
Find the circle of constant normalized resistance r3. Given R and ZR Find (d) and Z(d)Given (d) and Z(d) Find R and ZRįind dmax and dmin (maximum and minimum locations for thevoltage standing wave pattern)įind the Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR)Īmanogawa, 2000 - Digital Maestro Series 145Ģ. This provides the complex function ( ) ( )1 11, x xCenter = Radius = As the normalized reactance x varies from - to, we obtain afamily of arcs contained inside the domain of the reflectionĪmanogawa, 2000 - Digital Maestro Series 144īasic Smith Chart techniques for loss-less transmission lines To do so, westart from the general definition of line impedance (which is equallyapplicable to the load impedance) The goal of the Smith chart is to identify all possible impedances onthe domain of existence of the reflection coefficient. Thisis also the domain of the Smith chart.Īmanogawa, 2000 - Digital Maestro Series 138 The domain of definition of thereflection coefficient is a circle ofradius 1 in the complex plane. The chart provides a clever way tovisualize complex functions and it continues to endure popularitydecades after its original conception.įrom a mathematical point of view, the Smith chart is simply arepresentation of all possible complex impedances with respect tocoordinates defined by the reflection coefficient. The Smith chart is one of the most useful graphical tools for highfrequency circuit applications. Amanogawa, 2000 - Digital Maestro Series 137


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
